STUDDED PIPE PILES
Pipe piles is a structural building material used to support and stabilize a building's foundation. When the soil below a building is loosely packed, it may not offer enough strength to keep the building stable over time. A pipe piling can be used to distribute the weight of the building deeper into the earth, where the soil is often more tightly packed. Pipe piles are also used to support exceptionally large or heavy buildings, where even standard soil cannot offer adequate support. Finally, a pipe piling may be required when the land area is too small to accommodate spread footers or foundations, forcing buildings to dig deeper to achieve sufficient ground stability.
Engineers and installers determine the placement for each pipe pile based on the building loads at various locations. A very heavy load, such as a piece of industrial equipment, may need to sit directly over a pile to ensure adequate support. When building loads are evenly distributed, installers may use a concrete pile cap to support the building. This allows the pipe pilings to be equally spaced below the building, then connected together with the pile cap to act as a large foundation system.
Piles are driven into the ground using large machines known as pile drivers. These machines contain hydraulic systems which exert extremely high levels of force to drive the piles into the ground. By driving the piles directly into the soil without drilling holes first, the soil itself helps to support and stabilize the piles. As the pile is driven underground, the soil is displaced, which increases friction and pressure around the pile to hold it in place.
Pipe Piles have been used extensively as foundation piles for power stations, high-rise buildings, civil engineering works, bridges, marine structures, harbours, etc.
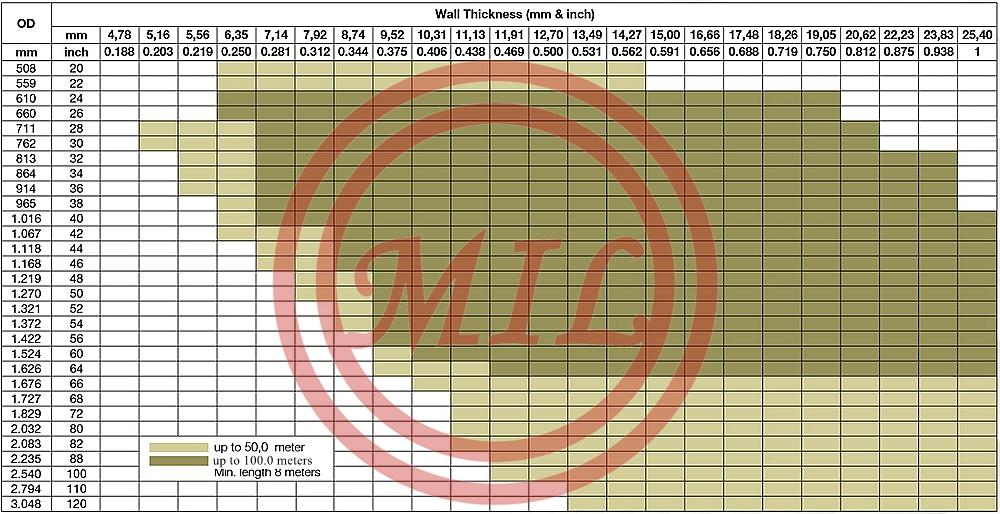
Each pipe piling must be carefully chosen based on building forces, soil conditions and local building codes. A geotechnical engineer can test the soil to determine whether piles are needed. The structural engineer then determines the size and material needed for each pipe piling, as well as the required depth. When a single pipe is not long enough to reach this depth, piles may be joined together using butt welds or splicing sleeves
- Combi piles
- Foundation piles for jetties, offshore platforms and LNG terminals
- Mooring piles, dolphins, etc.
- Foundation piles for bridges and onshore foundations
- Micro piles
- Struts in building pits
1.Pipe Specification
API 2B Specification for the Fabrication of Structural Steel Pipe
ASTM A139 CHIMNEYS AND VENTILATION DUCTS for air and dust filtering systems, and smoke evacuation, PILLARS for ski chair-lifts and bridges
ASTM A252 Foudation Piles for soil consolidation, marine wharfs---Grade1, Grade 2, Grade 3
ASTM A500 Cold Formed Welded and Seamless Carbon Steel Steel Structural Tubing in Round and Shapes
AWWA C200 : Steel Water Pipe 6 inches and Larger
AS1579 Arc-Welded Steel Pipes and Fittings for Water and Wastewater
AS 2159 Piling Design and Installation
AS 812 Bored Piles
BS 534 : Steel Pipes and Specials for Water and Sewage
BS 6363 Welded Cold Formed Steel Structural Hollow
CSA G40.21-92-CAN CSA-1992 structural quality steels general instruction no 1-2; and 4
DIN 1626 WELDED CIRCULAR TUBES OF NON ALLOY STEELS WITH SPECIAL QUALITY EQUIREMENTS
DIN 2460 Steel tubes for waterworks services
EN 10219 Cold formed welded structural hollow sections of non-alloy and fine grain steels--S235, S235JR, S235 G2H, S275, S275JR, S355JRH, S355J2H
EN 10224 Steel pipes, joints and fittings for the conveyance of aqueous liquids including potable water
EN 10296-1 Welded steel tubes for mechanical and general engineering purposes – TDR. Part 1: Non alloy and alloy steel tubes
IS 4923 Steel tubes for Hollow sections used in structures
JIS G3444 : Carbon Steel Tubes for General Structural Purpose---SS330, SS440, SS490, SPHD, SPHE
JIS G3457 : Arc Welded Carbon Steel Pipes
JIS A5525 : Steel Pipe Piles
KS D 3566 Carbon Steel Tubes for General Structural Purpose- STK 90,400,490,500,540
KS D 3583 Arc Welded Carbon Steel Pipe- SPW 400
KS F4602 Steel Pipes Piles
KS F4605 Steel Pipe Sheet Piles
TIS 427 : Electrically Welded Steel Water Pipes
MWA : Metropolitan Waterworks Authority of Thailand
PWA : Provincial Waterworks Authority of Thailand
RID : Royal Irrigation Department of Thailand
EGAT : Electricity Generating Authority of Thailand
2. Coating Specifications
2.1.External Coating
2.1.1 External Epoxy Coating
CAN/CSA-Z245.20 Standard for External Fusion Bond Epoxy Coating for Steel Pipe
AWWA C210 Standard for Liquid-Epoxy Coating Systems for the Interior and Exterior of Steel Water Pipelines
AWWA C213 Standard for Fusion Bonded Epoxy Coating for the Interior and Exterior of Steel Water Pipelines.
NACE RP0394 – National Association of Corrosion Engineers Standard Recommended Practice, Application, Performance, and Quality Control of Plant Applied, Fusion Bonded Epoxy External Pipe Coating.
NACPA 12-78 – National Association of Pipe Coating Applicators External Application Procedure for Plant Applied fusion Bonded Epoxy (FBE) to Steel Pipe.
2.1.2 Polyethylene Coating
CAN/CSA Z245.21 External Polyethylene Coating for Pipe
DIN 30670 Polyethylene Sheathing of Steel Tubes and of Steel Shaped Fittings
NFA 49-710 External Three-Layer Polyethylene Based Coating, Application by Extrusion
AS/NZS 1518 External Extruded High-Density Polyethylene Coating System for Pipes
UNI 9099-DIN 30670 Polyethylene Coating Applied by Extrusion
2.1.3 Polypropylene Coating
DIN30678 Polypropylene Sheathing of Steel Tubes and of Steel Shaped Fittings
EN 10286 Steel tubes and fittings for onshore and offshore pipelines –External three layer extruded polypropylene based coatings.
NFA 49-711 External Three-Layer Polypropylene Based Coating, Application by Extrusion
09-SAMSS-114 Shop-Applied Extruded, Three-Layer Polypropylene External Coatings for Line Pipe
2.1.4 Polyurethane Coating
AWWA C222-99: Polyurethane Coatings for the Interior and Exterior of Steel Water Pipe and Fittings
BS 5493- Polyurethane Coating
DIN 30677.2 polyurethane Insulation of the fittings
EN 10290- External Liquid Applied Polyurethane Coatings
2.1.5 Polyolefin Coating
AWWA C225-03: Fused Polyolefin Coating Systems for the Exterior of Steel Water Pipelines
AWWA C215-99: Extruded Polyolefin Coatings for the Exterior of Steel Water Pipelines
AWWA C216-00 Standard for Heat-Shrinkable Cross-Linked Polyolefin Coatings for the Exterior of Special Sections, Connections, and Fitting for the Steel Water Pipelines
AWWA C224 - 01: Two-layer Nylon-11 Based Polyamide Coating System for Interior and Exterior of Steel Water Pipe and Fittings
AWWA C225 - 03: Fused Polyolefin Coating Systems for the Exterior of Steel Water Pipelines
2.1.6 Tape Coating
AWWA C209-00: Standard for Cold-Applied Tape Coatings for the Exterior of Special Sections, Connections, and Fittings for Steel Water Pipelines
AWWA C214-00 Standard for Tape Coating Systems for the Exterior of the Steel Water Pipelines
AWWA C217-99 Standard for Cold-Applied Petrolatum Tape and Petroleum Wax Tape Coatings for the Exterior for Special Sections, Connections, and Fittings for Buried/Submerged Steel Water Pipelines
AWWA C218-02 Standard for Coating the Exterior of Aboveground Steel Water Pipelines and Fittings
AWWA C224-01: Two-layer Nylon-11 Based Polyamide Coating System for Interior and Exterior of Steel Water Pipe and Fittings
2.1.7 Bitumen Coating
DIN 30673 Bitumen coatings and linings for steel pipes, fittings and vessels.
2.1.8 Coal-Tar Enamel Coating
AWWA C-203 Coal-Tar Protective Coatings and Linings for Steel Water Pipelines-Enamel and Tape-Hot-Applied
AWWA C205 Cement Mortar Protective Lining and Coating for Steel Water Pipe - 4 inch (100 mm) and Larger- Shop Applied
2.1.10 Marine Coating
EN ISO 12944:1998 – Paints & Varnishes – Corrosion Protection of Steel Structures by protective paint system (parts 1 – 8)
ISO 20340:2009 Paints and varnishes – Performance requirements for protective paint systems for offshore and related structures
ISO 15741 Paints and varnishes-Friction-reduction coatings for the interior of on- and offshore pipelines for non-corrosive gases
2.2. Internal Coating
2.2.1 Epoxy Lining
AWWA C210: Liquid-Epoxy Coating Systems for the Interior and Exterior of Steel Water Pipelines
2.2.2 Bitumen Lining
DIN 30673 Bitumen coatings and linings for steel pipes, fittings and vessels
UNI-ISO 5256/87 STANDARD-BITUMEN COATING
2.2.3 Cement Mortar Lining
AS/NZS 1516 Cement Mortar Lining of Pipelines In Situ
AWWA C203-02: Coal-Tar Protective Coatings & Linings for Steel Water Pipelines, Enamel & Tape, Hot-pap. (Incl. add. C203a-99)
AWWA C205-00: Cement-Mortar Protective Lining and Coating for Steel Water Pipe- 4 In. (100 mm) and Larger-Shop application
AWWA C602 Standard for Cement-Mortar Lining of Water Pipelines - 4 inch (100 mm) and Larger - In Place
2.3Coating Material Applied:
3M: SK 134, SK6233, SK6352 Toughkote, SK 314, SK 323, SK 206N, SK 226N, SK 6251 DualKote SK-6171, SK 206P, SK226P,
3M Internal Coatings: Coupon EP2306HP
DuPont: 7-2500, 7-2501, 7-2502, 7-2508, 7-2514, 7-2803, 7-2504 Nap Gard Gold 7-2504, Nap Rock: 7-2610, 7-2617 FBE Powders
DuPont: Repair Kits; 7-1631, 7-1677, 7-1862, 7-1851
DuPont Internal Coatings: 7-0008, 7-0010, 7-0014, 7-0009SGR, 7-0009LGR, 7-2530, 7-2534, 7-2509
Akzo Nobel: FBE - Fusion Bond Epoxy
Internline 876 Seal Coat
Hampel: 85448,97840
Denso: 7200, 7900 High Service Temperature Coatings
Internal Liquid Epoxy: Powercrete Superflow
INTERZONE 954