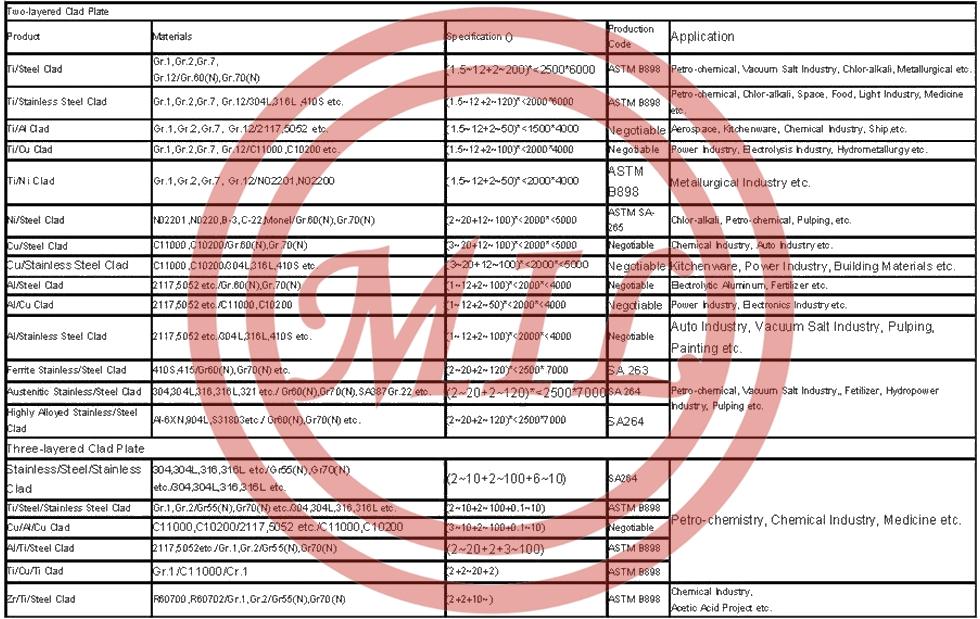
1. Defination
A clad metal plate is manufactured by laminating two metal plates or more and joining the laminated metal plates to each other. This clad metal plate is excellent in corrosion resistance, wear resistance and heat resistance, and has a high strength. Therefore, the clad metal plate is widely used as an inexpensive material.
As the methods for manufacturing clad metal plate, an explosion bonding process, a surfacing process and a rolling process are common. The rolling process, which can manufacture the clad metal plate of large area with high efficiency and at low cost, is most generally used.
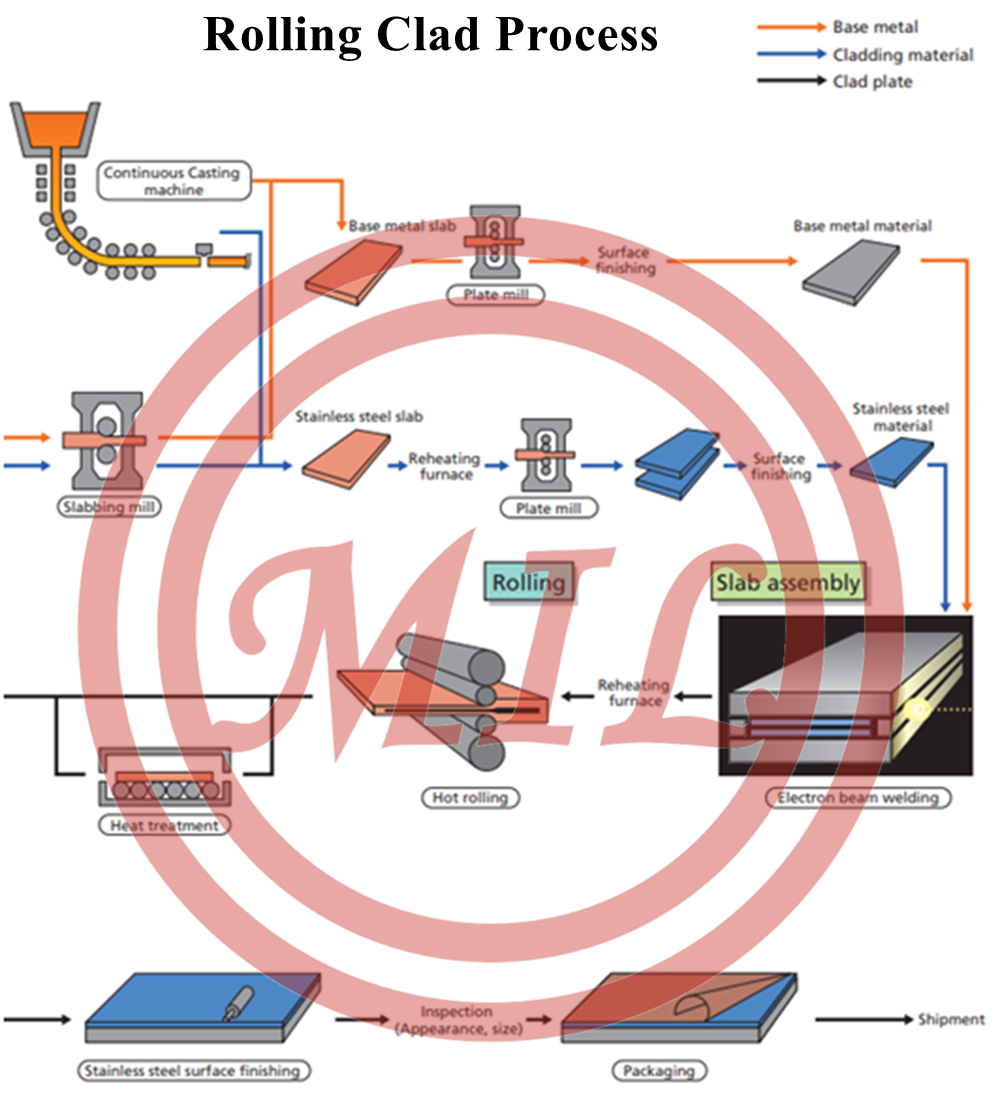
2. Rolling Process
A method of manufacturing clad metal plate products by assembling in a stacked array a bottom base plate, a first cladding plate, a second cladding plate and a top base plate, with a separator compound layer between the first and second cladding plates. The peripheral dimensions of the cladding plates being less than the peripheral dimensions of the base plates. A metal rail is welded between the base plates and circumferentially of the cladding plates to form an assembly having a closed environment encompassing the cladding plates. Substantially all water and oxygen are removed from the closed environment. The assembly is then heated to an initial temperature of at least about 1850° F. and, while heated, is rolled or hydraulically pressed to cause the first cladding plate to bond to the bottom base plate and the second cladding plate to bond to the top base plate. Separating the assembly at the separator compound layer provides a first and a second clad plate. In the preferred application of the method, a cladding activator is electrolessly deposited onto the surface of each of the cladding plates that contact a base plate to incorporate liquid interface diffusion bonding of the cladding plates to the base plates.
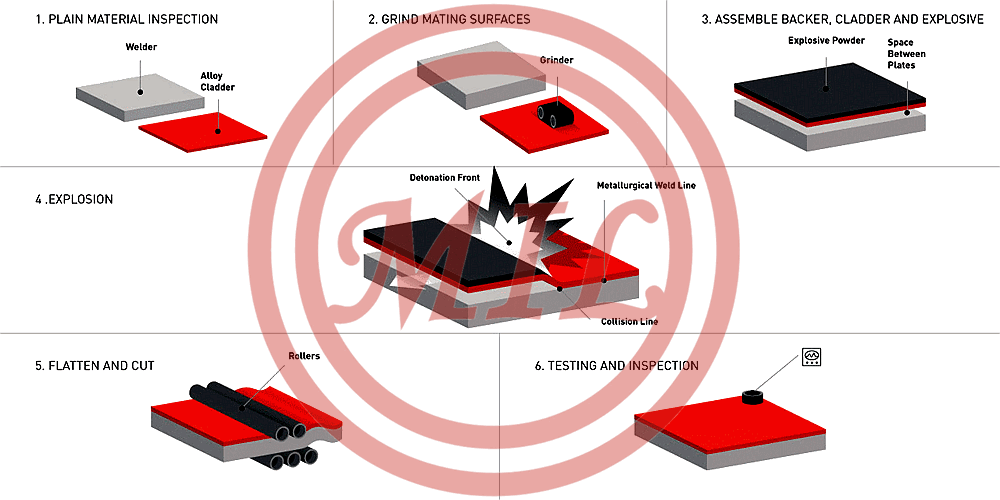
 3. Explosion Process
3. Explosion Process
The explosion bonding process, also known as "cladding by the explosion welding process", is a technically based industrial welding process. The process uses an explosive detonation as the energy source to produce a metallurgical bond between metal components. It can be used to join virtually any metals combination, both those that are metallurgically compatible and those that are known as non-weldable by conventional processes. Furthermore, this process can clad one or more layers onto one or both faces of a base metal, with the potential for each to be a different metal type or alloy.
The clad materials are possessed of the special properties in corrosion resistance, heat resistance and erosion resistance of the cladding material, and of the strength and the rigidity of the mother plate in respect to the structural requirements. The modern engineering design, manufacture and application need reasonable selection and use of the materials to optimize the design and improve the reliability of the products. The rupture test of engineering structure for the metal clad materials has medicated that the cracks are spread along the interface, even if it made structure-breaking . This is very important for the safety of the structure. Thus, the materials selected are required to be possessed of excellent comprehensive performances and reasonable economy. The metal clad materials have embodied all these advantages. In terms of economy, the cladding materials have the advantage of smaller thickness and less cost as compared to monometallic materials.
Due to its use of explosive energy, the process occurs extremely fast; unlike conventional welding processes, parameters cannot be fine-tuned during the bonding operation. The bonded product quality is assured through selection of proper process parameters, which can be well controlled. These include material surface preparation, plate separation distance prior to bonding, and explosive load, velocity, and detonation energy. Selection of parameters is based upon the mechanical properties, mass, and acoustic velocity of each component metal being bonded. Optimum bonding parameters, which result in consistent product quality, have been established for most metals combinations. Parameters for other systems can be determined by calculation using established formulas.
4.Application Field:
Clad steel plate offers a low cost and highly effective solution in industrial sectors such as construction, shipbuilding and the manufacture of certain types of industrial tanks including pressure vessels.
Clad product manufactured in compliance to ASME SA 263, SA 264, SA 265 & B 432 under TPO LRIS / BVIS / TUV / ABS / Equivalent.
All the clad metal materials would be used in the fields of petro chemical industry, salt industry, chlorin-alkali, food machinery, aviation and aerospace industry, medical machinery, light industry, heavy industry, cookware industry, ship building industry, electric industry,cryogenic industry and so on.
5. Clad Plate Specification
|
U S A
|
J A P A N
|
C H I N A
|
|
ASTM A264 Specification for stainless chromium-Nickel steel-clad plate sheet and strips
|
JIS GS3601 Stainless-steel clad plate
|
GB/8165-1997 Stainless steel clad plates and strips
|
|
ASTM A265 Nickel and Nickel alloy clad steel plate
|
JIS G3602 Nickel and Nickel alloy clad plate
|
GB/T8165-1997 Stainless Steel Clad Plates and Strips
|
|
ASTM B432 Specification for copper and copper alloy clad plate
|
JIS G3604 Copper and copper alloy clad steel plate
|
GB13238-1991 Copper-steel clad plate
|
|
ASTM A263 Specification for corrosion-resisting chromium steel-clad plate sheet and strip
|
JIS G3603 Titanium clad steel plate
|
GB8547-1987 Titanium-steel clad plate
|
|
ASTM B898 Standard Specification for Reactive and Refractory Metal Clad Plate
|
|
GB8546-1987 Titanium-stainless steel clad plate
|
|
Base Material
|
|
U S A
|
J A P A N
|
C H I N A
|
|
ASTM A36 Structural steel
|
JIS C3101 SS400 Rolled steel for general structure
|
GB700-1988 Carbon structural steel
|
|
ASTM A283 Carbon steel plates, section steel and steel bars for intermediate and low strength
|
JIS 3106 SM400, 490, 490YRolled steel for welded structure
|
GB3274-1988 Carbon structural and low alloy steel rolled plate and strips
|
|
ASTM A285 A516 Carbon steel plates for pressure vessels
|
JIS G3115 SB410, 450, 480, 450M, 480M Carbon steel and molybdenum alloy steel plates for Boilers and pressure vessels
|
GB711-1988 Hot-rolled quality carbon structural steel plate and wide strips
|
|
ASTM A204 A387 Molybdenum and molybdenum-Chromium alloy steel plates for vessels
|
JIS G3115 SPV235, 315, 355, 450, 490 Steel plates for pressure vessels
|
GB713-1997 Steel plate for boilers
|
|
ASTM A515 Carbon steel plates for intermediate and high temperature for pressure vessel
|
JIS G3118 SGV410, 450, 480 Carbon steel plate for pressure vessels for intermediate and moderate temperature service
|
GB/T1591-1994 High strength low alloy structural steels
|
|
ASTM A302 Manganese-molybdenum manganese molybdenum-Nickel alloy steel plates for pressure vessel
|
JIS G4109 SCMV2, 3, 4 Chromium-Molybdenum
|
GB6654-1996 Steel plate for pressure vessels
|
|
|
JIS G312 SLA235, 325, 360 Carbon steed plates for low temperature service
|
GB3531-1996 Low alloy steel plate for low temperature pressure vessels
|
The interface strength between the dissimilar materials explosively welded on is strong enough to keep away from separateness, which it may be endure some external stress such as heat, bending, vibration or hard impact, in the late process.
Such clad metal plates would be used in chemical vessels, reactors, heat exchangers, condensers, storage tanks etc.
For base materials mainly structural steels, pressure vessel steels and fine grain structural steels are used; they have proper weldability and workability.
For clad materials we offer ferritic and austentic stainless steels, nickel and nickel-based alloys, copper and copper-nickel-alloys as well as titanium, which are characterized by their corrosion resistance properties.
The surface of the base material is normally "as rolled" or shot blasted.
The surface of the clad material is normally ground with a grain size of 80. Other grain sizes are available on request.
7. Size:
The thickness ratio of mother layer to cladding layer of explosion metal clad materials is based on the requirements of the design and applications. The ratio of 3:1 or more is generally recommended. Large or small sizes of metal clad materials are available. Orders of any quantities are welcome with no limit of the minimum quantity. The large size that 3800 mm(W) by 11000 mm (L) and 3600 mm (W) by 3600 mm (L). Besides, our company also produces metal clad rods and tubes. Metal clad materials with special sizes are also available through negotiations in order to meet the customers' needs.