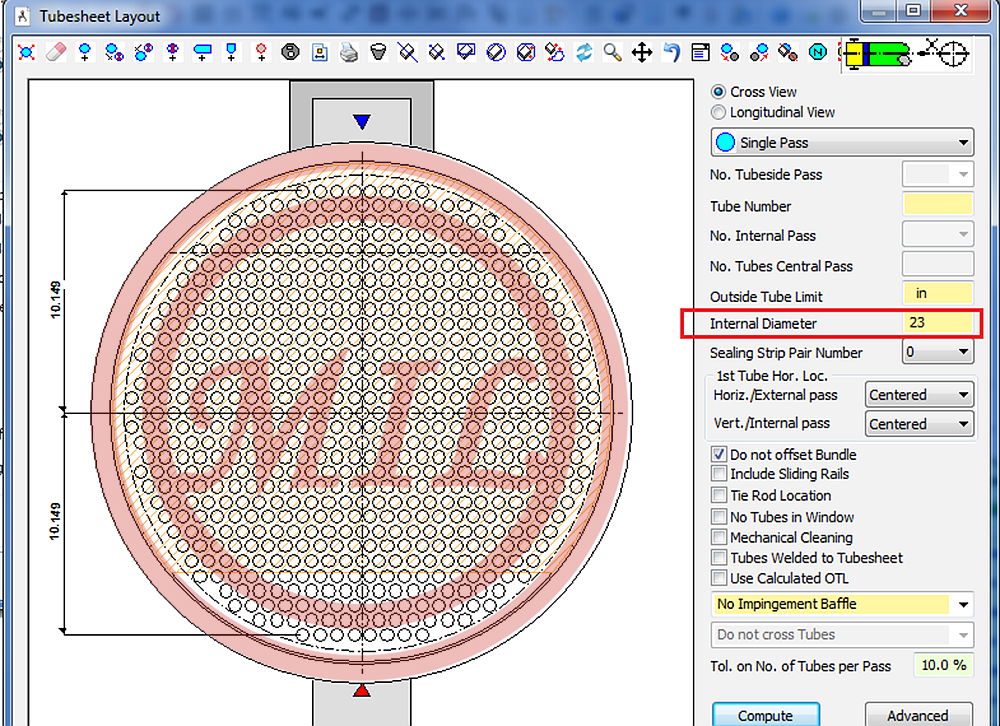
Tube Sheet is a plate, sheet, or bulkhead which is perforated with a pattern of holes designed to accept pipes or tubes. These sheets are used to support and isolate tubes in heat exchangers and boilers or to support filter elements. Depending on the application, a tube sheet may be made of various metals or of resin composites or plastic. A sheet tube may be covered in a cladding material which serves as a corrosion barrier and insulator and may also be fitted with a galvanic anode. Tube sheets may be used in pairs in heat exchange applications or singularly when supporting elements in a filter.
Perhaps the best known use of tube sheets are as supporting elements in heat exchangers and boilers. These devices consist of a dense arrangement of thin walled tubes situated inside an enclosed, tubular shell. Tubes are supported on either end by sheets which are drilled in a predetermined pattern to allow the tube ends to pass through the sheet. The ends of the tubes which penetrate the tube sheet are expanded to lock them in place and form a seal.
The tube arrangement forms a contained unit between the tube sheets. The tube sheets are then bolted to flanges inside the shell. The shell extends beyond each tube sheet and is sealed, thereby forming two closed chambers on the non-tube ends of the tube sheets. This creates an arrangement where the exchanger consists of two separate end chambers joined by tubes which pass through an isolated space between the tube sheets. Heated fluid is then passed from one end chamber to the other through the tubes where cold fluid in the cavity between the tube sheets absorbs the heat energy.
The design of tube sheets is a fairly precise and complex process; the exact number of tubes needs to be established and a pattern of holes calculated to spreads them evenly over the tube sheet surface. Large exchangers may have several thousand tubes running through them arranged into precisely calculated groups or bundles. Sheet design and production is largely automated these days with computer-aided design (CAD) software performing the calculations and the tube sheet drilling done on computer numerical control (CNC) machines.
The tube sheets used in heat exchangers and boilers are often clad with an insulating layer which also serves to protect against corrosion. To further protect the tube sheet from rust, a sacrificial or galvanic anode may also be attached to the surface of the sheet. Tube sheets are also used on cartridge-type filter devices to support the individual filter elements. They are similar in design to the high heat boiler varieties except they are typically made of resin composites or plastic and are generally used as single units. There are usually fewer tubes involved in a filter application although the tube sheet design still has to be carefully calculated to ensure optimal performance.
Clad Tube Sheet Material
Explosion Bonded - Corrosive Resistant CLAD Lining (Provides a Metallurgical Bond)
The most common application of explosively bonded (clad) metals, is as corrosive or erosive resistant linings of pressure vessels, chemical process tanks, heat exchangers, and tube sheets. Not only do valued customers benefit from the corrosive resistance clad, but also from significant cost reduction by being afforded the opportunity to utilize structural steels to improve wall strength without having to manufacture the entire structure out of the, typically expensive, corrosive resistant materials.
ASTM Standards
A266/A266M Specification for Carbon Steel Forgings for Pressure Vessel Components
A275/A275M Practice for Magnetic Particle Examination of Steel Forgings
A288 Specification for Carbon and Alloy Steel Forgings for Magnetic Retaining Rings for Turbine Generators
A289/A289M Specification for Alloy Steel Forgings for Nonmagnetic Retaining Rings for Generators
A290/A290M Specification for Carbon and Alloy Steel Forgings for Rings for Reduction Gears
A291/A291M Specification for Steel Forgings, Carbon and Alloy, for Pinions, Gears and Shafts for Reduction Gears
A336/A336M Specification for Alloy Steel Forgings for Pressure and High-Temperature Parts
A372/A372M Specification for Carbon and Alloy Steel Forgings for Thin-Walled Pressure Vessels
A427/A427M Specification for Wrought Alloy Steel Rolls for Cold and Hot Reduction
A469/A469M Specification for Vacuum-Treated Steel Forgings for Generator Rotors
A470/A470M Specification for Vacuum-Treated Carbon and Alloy Steel Forgings for Turbine Rotors and Shafts
A471/A471M Specification for Vacuum-Treated Alloy Steel Forgings for Turbine Rotor Disks and Wheels
A504/A504M Specification for Wrought Carbon Steel Wheels
A508/A508M Specification for Quenched and Tempered Vacuum-Treated Carbon and Alloy Steel Forgings for Pressure Vessels
A521/A521M Specification for Steel, Closed-Impression Die Forgings for General Industrial Use
A541/A541M Specification for Quenched and Tempered Carbon and Alloy Steel Forgings for Pressure Vessel Components
A551/A551M Specification for Carbon Steel Tires for Railway and Rapid Transit Applications
A579/A579M Specification for Superstrength Alloy Steel Forgings
A592/A592M Specification for High-Strength Quenched and Tempered Low-Alloy Steel Forged Parts for Pressure Vessels
A646/A646M Specification for Premium Quality Alloy Steel Blooms and Billets for Aircraft and Aerospace Forgings
A649/A649M Specification for Forged Steel Rolls Used for Corrugating Paper Machinery
A668/A668M Specification for Steel Forgings, Carbon and Alloy, for General Industrial Use
A711/A711M Specification for Steel Forging Stock
A723/A723M Specification for Alloy Steel Forgings for High-Strength Pressure Component Application
A729/A729M Specification for Carbon and Alloy Steel Axles, Heat-Treated, for Mass Transit and Electric Railway Service
A765/A765M Specification for Carbon Steel and Low-Alloy Steel Pressure-Vessel-Component Forgings with Mandatory Toughness Requirements
A768/A768M Specification for Vacuum-Treated 12 % Chromium Alloy Forgings for Turbine Rotors and Shafts
A788/A788M Specification for Steel Forgings, General Requirements
A837/A837M Specification for Steel Forgings, Alloy, for Carburizing Applications
A859/A859M Specification for Age-Hardening Alloy Steel Forgings for Pressure Vessel Components
A891/A891M Specification for Precipitation Hardening Iron Base Superalloy Forgings for Turbine Rotor Disks and Wheels
A909/A909M Specification for Steel Forgings, Microalloy, for General Industrial Use
A939/A939M Practice for Ultrasonic Examination from Bored Surfaces of Cylindrical Forgings
A940/A940M Specification for Vacuum Treated Steel Forgings, Alloy, Differentially Heat Treated, for Turbine Rotors
A965/A965M Specification for Steel Forgings, Austenitic, for Pressure and High Temperature Parts
A966/A966M Practice for Magnetic Particle Examination of Steel Forgings Using Alternating Current
A982/A982M Specification for Steel Forgings, Stainless, for Compressor and Turbine Airfoils
A983/A983M Specification for Continuous Grain Flow Forged Carbon and Alloy Steel Crankshafts for Medium Speed Diesel Engines
A1021/A1021M Specification for Martensitic Stainless Steel Forgings and Forging Stock for High-Temperature Service
A1049/A1049M Specification for Stainless Steel Forgings, Ferritic/Austenitic (Duplex), for Pressure Vessels and Related Components